Most elliptical galaxies can usually be found within galaxy clusters. However, a new picture of galaxy NGC 474 captured by Hubble shows an interesting image. Instead of being surrounded by galaxy clusters, NGC 474 is in relatively empty space. Further, the galaxy is surrounded by shells.
NASA says could be the result of NGC 474 absorbing smaller galaxies. Many believe this could have happened billions of years ago. Ultimately, though, nobody is completely sure how these tidal-like shells formed around the galaxy.
Check out this galaxy surrounded by shells
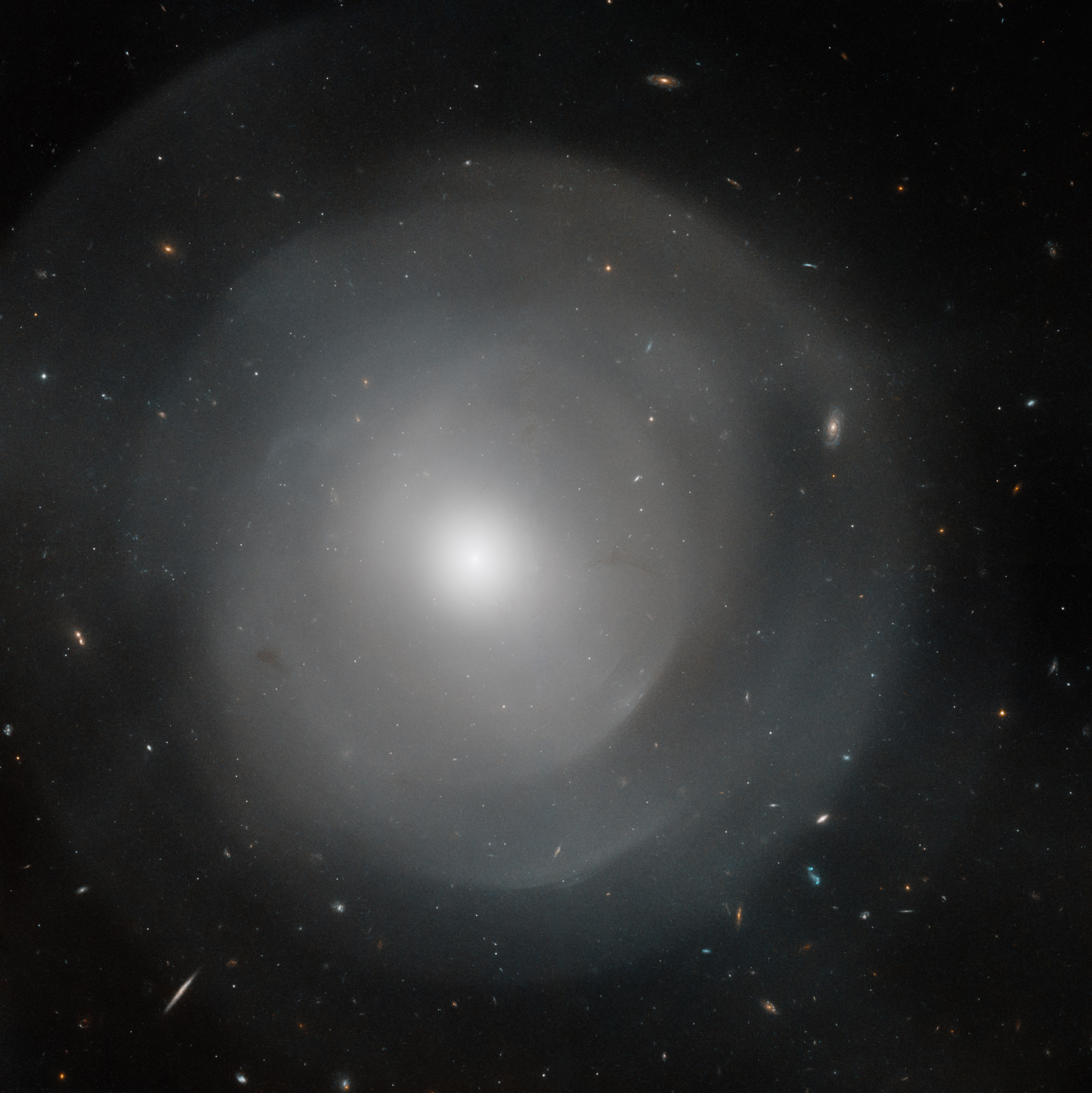

NASA’s Hubble space telescope has discovered some fantastic things. For starters, its nearly 30-years’ worth of observations have taught us a lot about how the universe expanded. Additionally, the telescope recently captured an image of two galaxies locked in a dance. Now, though, a new photo gives us a great look at a galaxy surrounded by shells.
The galaxy in question is NGC 474, and it’s an elliptical galaxy. Hubble recently captured an image of the galaxy up close, revealing more about its size. Scientists estimate the galaxy to be 2.5 times larger than our own Milky Way galaxy. But, as I noted above, this size isn’t the only interesting feature.
That’s because several layered shells surround the galaxy. Scientists aren’t exactly sure what caused the shells. However, they believe that it could have been caused by galactic mergers. Such a merger could possibly have created the different layered shells. NASA says it would be similar to how a pebble dropped into a pond might create ripples across the water.
Studying NGC 474

As I noted above, NGC 474 is located in mostly empty space. Overall, it’s roughly 100 million light-years away from the Earth. It also measures approximately 250,000 light-years across.
Because of its interesting features, scientists have studied the tidal shells that surround the galaxy. Multiple studies have come out about how the shells formed, though the general consensus still seems to be that NGC 474 absorbed another galaxy billions of years ago. What makes this galaxy surrounded by shells even more intriguing, though, is that it’s moving away from the Sun.
Scientists believe that the galaxy is moving away at a rate of 2412 kilometers a second thanks to dark energy. As such, it may continue to get further and further away from the Sun. Astronomers also discovered a supernova within the galaxy. They named it SN 2017fgc upon its discovery in 2017.